#BoycottTarget campaign reaches 500,000 signers
Body
“Less than a week after Target, the nation’s second-largest discount retailer, announced that transgender customers may use the restroom that ‘corresponds with their gender identity,’ nearly 500,000 people have signed a #BoycottTarget online petition launched by the conservative American Family Association.” RNS
Discussion
McCrory seeks changes to NC restroom bill
Body
“Executive Order 93 affirmed most of the provisions of HB2, including one that protects public establishments from being forced to allow biological males and females to have access to restrooms and locker rooms of the gender with which they identify. But …” WORLD
Discussion
Rights groups sue North Carolina governor regarding new transgender law
Body
“The bill (H.B. 2) also known as the Public Facilities Privacy & Security Act, requires students to use bathrooms and changing facilities that correspond with their biological sex, regardless of the students’ gender identity.”
Discussion
Homosexuality, Changing Times, & The Bible (Part 2)
(Read Part 1.)
What Does the Bible Say?
We need to turn now from the rapidly changing values concerning sexuality, as is exhibited in our culture, to the never-changing teachings of Scripture. As Christians, we recognize the absolute authority of the Bible, God’s revealed Word, and humbly submit to whatever it proclaims, whether it is popular or not, or as Paul says, “in season and out of season” (2 Tim 4:2).
Discussion
Robert Gagnon vs. J. Daniel Kirk on Homosexuality
Body
“[T]he decision to view it as a viable Christian position over which we should not divide is itself a judgment, a decision.”
Discussion
Talking to Your Kids About Sexual Sin (Part 2)
(From Voice magazine, Nov/Dec 2015. Used by permission. Read Part 1.)
Our culture continues to hold fast to the same sins we read about in Genesis, reveling in perversion and condemning any who refuse to join in the celebration. So while we may (and should) shelter our family from sins of this nature, it is inescapable that we as parents will have to address these sins with our children at some level. And the place to begin, is in the beginning, where God created a perfect world and joined the first man and the first woman in the perfect union: marriage.
Show and Tell
But then the question arises: “Where do I go from here?” Outside the safety of the Garden, gross sin lurks on nearly every page. You may be wondering, does my four-year-old son even need to know about homosexuality? He does, but he doesn’t need to know every last detail just yet. Sometimes it’s as much about what’s not said as what is said.
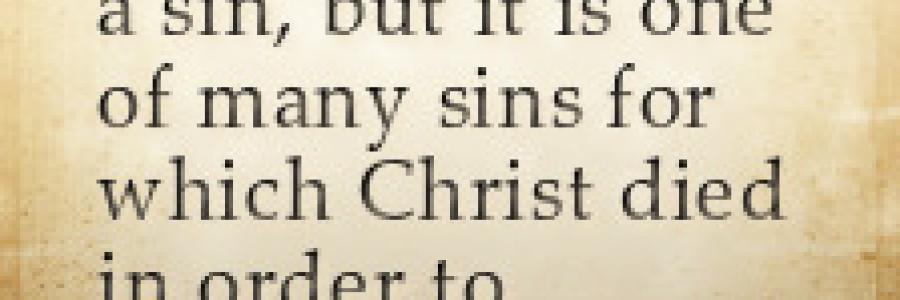





Discussion