Bishops and Fathers
Discussion
Acts 6 and Church Decisions
Discussion
Postmodernism 7 - The Postmodern Church
From Sunesis. Posted with permission. Read the series.
The quotation below is from www.vintagefaith.com. (This site is currently down, with a promise that it will be revised and restarted January 1, 2013—yes, that’s the correct date; even the postmoderns struggle with maintaining relevance.)
There is a rising feeling among emerging church leaders and followers of Jesus, that in many modern contemporary churches, something has subtly gone astray in what we call “church” and what we call “Christianity.” Through time, church has become a place that you go to have your needs met, instead of being a called local community of God on a mission together. Through time, much of contemporary Christianity subtly has become more about inviting others into the subcultures of Christian music, language and church programs than about passionately inviting others into a radically alternative community and way of life as disciples of Jesus and Kingdom living. Sadly, we are now seeing the results of this. While many of us have been inside our church offices busy preparing our sermons and keeping on a fast-paced schedule in the ministries and internal affairs of our churches, something alarming is happening on the outside. A great transformation is happening in our own neighborhoods, schools, and colleges. What once was a Christian nation with a Judeo-Christian worldview, is fast becoming an unchurched post-Christian nation. Tom Clegg and Warren Bird in their book Lost In America claim that the unchurched population of the United States is now the largest mission field in the English-speaking world and fifth largest globally. There are many great churches ministering to modern-minded people, but we must be also be passionate about emerging generations who aren’t connecting with current forms of ministry and thinking. Yet, there are some exciting things developing and stirring. So many people are beginning to experience the same sort of unsettledness and beginning many positive and healthy conversations. More and more emerging leaders are re-seeking the Scriptures, studying the early church and church history and rethinking a lot of what we are doing. In our desire to engage the current culture and emerging generations, perhaps we need to spend time looking more to the values and ancient roots of our faith, instead of looking out primarily for what is “cutting edge,” the next “model” or the latest programs. Vintage Faith is simply looking at what was vintage Christianity. Going back to the beginning and looking at the teachings of Jesus with fresh eyes and hearts and minds. Carefully discerning what it is in our contemporary churches and ministry that perhaps has been shaped through modernity and evangelical subculture, rather than the actual teachings of Jesus and the Scriptures. We need to begin asking a lot of questions again. We shouldn’t be afraid to ask questions. Too much is at stake not to.
Discussion
Building Up the Body: Four Marks of Maturing Churches
From Voice, Nov/Dec 2013. Used by permission. (Read part 1.)
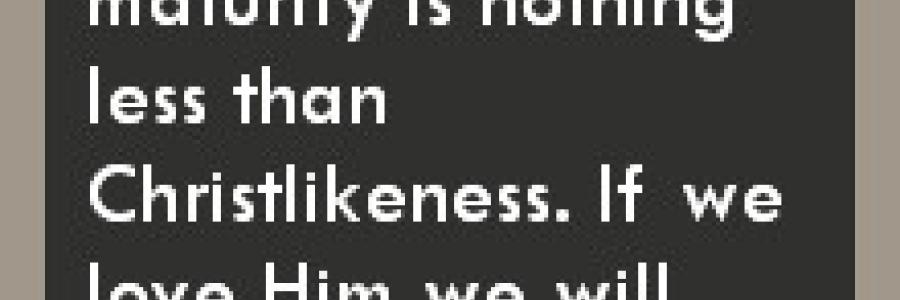
Churches that take the Lord’s instruction in Ephesians 4 seriously will be the ones marching in the direction of maturity (Ephesians 4:13). Those who do not, will find themselves drowning in a sea of immaturity (4:14). These are the two options Paul lays before his readers. The first option finds the local church being equipped by the teaching of the Word and in turn building up the body of Christ. Such churches will be marked by four things.
First, unity: “Until we all attain to the unity of the faith.” Throughout the epistles the term “the faith” does not refer to subjective faith (e.g. “I believe; I have faith in God”) but to objective truth. “The faith” is a phrase synonymous with sound doctrine, or the body of truth as taught in the Bible. True unity is grounded in correct theology.
A certain pastor, in writing a critique of my ministry, said that he “leaned toward unity but you lean toward purity.” That may be a true evaluation, but I do not believe there is unity without purity. An attempt at unity without doctrinal purity is merely uniformity. Many today are willing to lay down their conviction of Scriptural truth in order to get along. Organizations are built under the umbrella of minimal beliefs but at the cost of great compromise, which leads to the doctrinal impurity of the church. While not all doctrinal beliefs are essential to the faith, and some are not hills worth dying on, I am amazed at what many are willing to jettison in order to embrace some form of outward unity. Paul, however, calls for a unity that is wrapped around the cardinal truths of the faith.
Discussion
Building Up the Body: Evangelicalism's Failure
From Voice, Nov/Dec 2013. Used by permission.
One of the most insightful of recent books concerning the church is actually written by an unbeliever. Alan Wolfe, a social scientist, has been observing the changing American religious scene for years. A few years ago he shared his research in The Transformation of American Religion (New York: Free Press, 2003). The message of his book is that “religion in the United States is being transformed in radically new directions” (3). Wolfe claims,
Talk of Hell, damnation, and even sin has been replaced by a nonjudgmental language of understanding and empathy. Gone are the arguments over doctrine and theology… More Americans than ever proclaim themselves born again in Christ, but the Lord to whom they turn rarely gets angry and frequently strengthens self-esteem. [As a result] the faithful in the United States are remarkably like everyone else. (3)
If Wolfe’s assessments are on target, what would be the catalyst for this transformation (or better, degeneration)? Wolfe’s thesis is that in an effort to win over American culture, Evangelicalism has stooped so low that it can no longer be distinguished from that culture. Take doctrine for example. Small-group Bible studies avoid theology like the plague, lest it prove divisive. Sermons are no better.
Discussion
Where Does the Seminary Fit in Relation to the Local Church?

This article discusses the relationship of the seminary to the local church. Specifically it argues for tangible recognition on the part of seminaries that the local church is the biblically designed co-center (along with the family) of biblical education. I advocate that acknowledgment include, wherever possible, a direct local church accountability, and ideally, a posture of working as a ministry of a local church, under that local church’s direct leadership.
On the importance of local church leadership of the seminary
One important reason for the decline of biblical education in the churches has been the seminary’s haste to take on responsibilities that are the jurisdiction of the church. As pastoral roles (regrettably) shift more and more toward corporate leadership, recruitment, and hospitality, and away from exegetical teaching and discipleship, the need for para-church organizations only increases. Local churches become less and less capable of fulfilling their biblical mandates, and thus become increasingly dependent upon seminaries in particular, for doctrinal and functional strategies and for filling their personnel needs.
Discussion
My Tribe
 If you spend any time around the internet, you’ll probably recognize this word: “tribe.” Now for hundred of years “tribe” was a pretty unassuming member of the English language, content to describe a discrete sociological structure.
If you spend any time around the internet, you’ll probably recognize this word: “tribe.” Now for hundred of years “tribe” was a pretty unassuming member of the English language, content to describe a discrete sociological structure.
Discussion
Early Christian Decision-Making: Where Do We Start?
 Also in this series: Part 1, Part 2.
Also in this series: Part 1, Part 2.
Pick up a book or a magazine article on the subject of church government and most likely you will read a discussion beginning with pastors, elders, ordination, or authority. Others go directly to instances of church order in the New Testament. Since graduating from seminary, my view on where to begin the subject has changed, step by step. Why is it that when we really want to understand the nature of something in Christ’s church we do not first look at Christ Himself and His church? If “a picture is worth a thousand words,” then why can’t we look at pictures of Christ and His church in the New Testament and begin to get our answers? And why can’t we first ask what Jesus said?1 As we read the New Testament and begin to reflect, we will understand that we have a few volumes’ worth of ideas to tell us how the church should govern itself, including the one small element I have chosen to write about: early Christian decision-making. I will focus on two of those ideas.
1. Authority and equality
Christians are followers of Jesus the Messiah. From the very first days of the Jesus movement until today, Jesus is known as the head (kephale) of the church (Eph. 4:15, 5:23, Col. 1:18) and the Lord (kyrios) of His followers (Matt. 8:23; Luke 11:1; Acts 1:21, 5:14, 15:11; Rom. 1:3; 1 Cor. 1:2; etc.). The authority of Jesus in the church is regal, absolute, and unquestioned. And to a certain extent, His authority limits creativity in church government.



Discussion